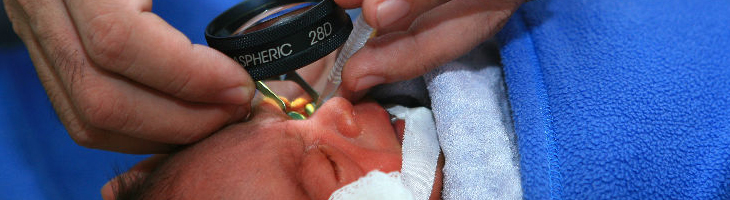
The retina is the delicate tissue lining the back of the inside of the eye which detects light
and allows us to see. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) is an eye condition which
affects the blood vessels of the retina.
The white oval in the centre is the optic nerve and the dark area towards the right of it is
known as the macula. The macula is the part of the eye that allows us to see fine
detail. The grey lines are the arteries and the black lines are the veins.
How common is ROP?
ROP is common in premature babies, affecting about 65% babies less than 1251
gram birthweight. The condition is usually very mild and settles on its own without
any treatment. In a very few babies (usually the smallest and most premature) the
ROP does not get better and treatment is needed. If not treated, very severe ROP can seriously affect a baby’s sight and even cause blindness.
No one knows exactly why. When a baby is born early, the blood vessels of the retina are not fully developed. After birth something triggers the blood vessels to start to grow abnormally and this forms scar tissue which, if severe, can damage the retina. The main cause of ROP is prematurity itself, so the more prematurely the birth occurs the greater the risk of ROP occurring. The amount of oxygen treatment required and the Diagrammatic view of the retina as though seen through the pupil.baby's general condition may also influence whether ROP develops or becomes severe.
However, some premature babies who have no serious illnesses still develop ROP, while others who have been very ill do not. Therefore it is necessary to screen all babies under 32 weeks’ gestation or under 1501 grams birthweight. What is Screening for ROP? ROP screening is the eye examination by an ophthalmologist (or eye specialist) to look for any signs of ROP. All babies weighing less than 1501 grams at birth or born more than 8 weeks early will need at least one eye screening examination.
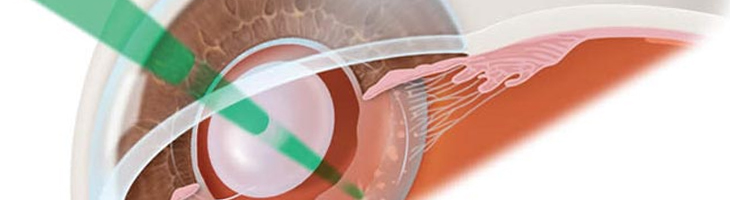
One of the most common problems after cataract surgery is clouding of the membrane around the lens. The membrane is referred to as the posterior capsule, and once the membrane becomes opacified, the condition is termed posterior capsule opacification. A cloudy posterior capsule causes blurry vision, but this condition can be treated easily and safely with a laser treatment in the office or outpatient center. Laser capsulotomy does not require going to the operating room and nor does it involve any incisions into the eye. It only takes a few minutes and is painless. Dilation of the eye is done with eye drops. A laser removes the hazy posterior capsule from your line of sight without making an incision or touching the eye. Drops may be given after the procedure to reduce inflammation. Your vision will improve very quickly after the procedure. You do not have to alter your usual activities. The procedure is extremely safe.
Topical anesthesia is a satisfactory and safe alternative to retrobulbar and peribulbar anesthesia for clear corneal phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation in selected cataract patients in the hands of experienced cataract surgeon.
In cataract surgery, the lens inside your eye that has become cloudy is removed and replaced with an artificial lens (called an intraocular lens, or IOL) to restore clear vision. Cataract surgery will restore the clarity of vision, and vibrancy of colors, that you experienced years earlier.
The health of your macula is paramount. The macula is at the center of your retina, in the back of the eye, and it's important to good vision and long-term eye health in two ways.
First, optimizing your macular pigment improves contrast sensitivity and your overall quality of vision. That aids in color perception and low-light situations.
Second, for the long term, preserving the health of your macula is key to prevention of macular degeneration, the major cause of blindness in older Americans.
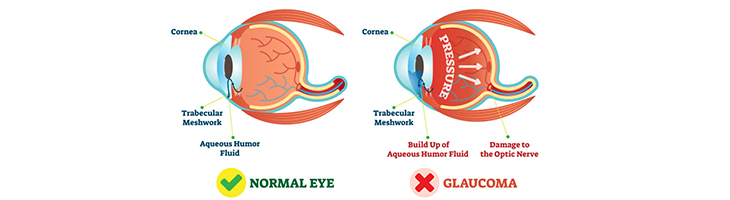
Surgery reduces the pressure in the eyes by opening blocked drainage angles or creating a new opening that fluid can flow through to leave the eye. In some cases surgery may be done to relieve pain caused by glaucoma. Doctors can use either a surgical cutting tool or a very focused beam of light, called a laser, to do surgery for glaucoma. Laser surgery is usually the first type of surgery tried. If laser surgery doesn't help, your doctor may try conventional surgery.It is not unusual for some people to have both open- and closed-angle glaucoma. They may need more than one kind of procedure Open-angle chronic glaucoma is the most common type where the loss of vision is gradual and painless. Usually it is detected when patients come to the eye doctor for a routine eye check up.
Acute / Closed Angle Glaucoma : in certain individuals, the angle from where fluid drains from the eye is genetically narrow. It can be blocked suddenly due to many reasons resulting in sudden increase in eye pressure.
As in a tonometry test, you'll first get drops to numb your eye. Your provider will then use a small device on your eye called a pachymeter. This device measures the thickness of your cornea. The cornea is the eye's outer layer that covers the iris (colored part of the eye) and the pupil. A thin cornea may put you at higher risk for getting glaucoma.
Perimetry, also known as a visual field test, measures your peripheral (side) vision. During perimetry, you'll be asked to look straight ahead at a screen. A light or image will move in from one side of the screen. You'll let the provider know when you see this light or image while still looking straight ahead.

LASIK, which stands for laser in-situ keratomileusis, is a popular surgery used to correct vision in people who are nearsighted, farsighted, or have astigmatism.All laser vision correction surgeries work by reshaping the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, so that light traveling through it is properly focused onto the retina located in the back of the eye. LASIK is one of a number of different surgical techniques used to reshape the cornea.
Opti Lasik combines today’s advanced surgical technologies into a procedure optimized for individual vision needs with minimum tissue ablation.
Epi-LASIK is a newer laser eye surgery procedure that was developed to solve some of the potential problems with LASIK and LASEK. It’s somewhat of a cross between the two, but differs in a few key areas. With advent of Intralase Bladfree technique Epi-lasik is now obsolete.
Presbyopia-test1PreLEX treatment (Presbyopic Refractive Lens Exchange) is a lens replacement procedure wherein the natural lens is replaced with a multi-focal intra-ocular lens implant. This is done to improve vision for those generally above the age of 40, as it is after this age that one’s eye sight begins to naturally become weak—causing blurred near vision while reading or working at the computer, or blurred far vision when looking at something from a distance.
Advanced technologies are created in the healthcare field to make the life of patient more comfortable and healthier. Technological advancements are a must in this field because many patients are not able to get the benefit of the technologies available in the industry. Such patients either suffer from altogether new disease or the disease is gone into an advanced stage and is not being treated with the current system of medications and surgery. Spectacles removal surgery is not isolated from these advancements. Scientists are trying their best to make available surgical treatment with the least complications and desired results. One such advanced surgery is Contoura Vision surgery, which is also known as Topography-guided LASIK surgery. This surgery is an advanced version of LASIK surgery and provides enhanced benefits to the patients who are considering to undergo spectacle removal surgery. Not only this surgery is effective in general patients but is also offer good results in patients who were not eligible for undergoing LASIK surgery due to irregularities in the cornea. The technology has been approved by USFDA for removal of the specs.
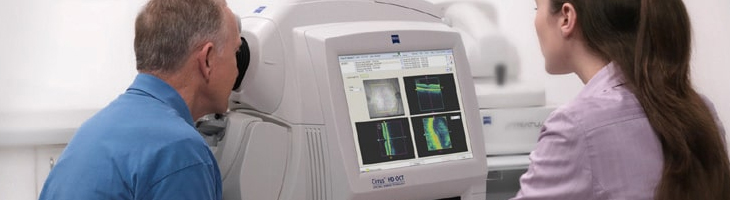
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina.
With OCT, your ophthalmologist can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows your ophthalmologist to map and measure their thickness. These measurements help with diagnosis. They also provide treatment guidance for glaucoma and diseases of the retina

Strabismus is the medical term of a squint, a condition where the eyes point in different directions. One eye may turn inwards, outwards, upwards or downwards while the other eye looks forward. Squints are common and affect about one in 20 children. They usually develop before a child is five years old, but can appear later, and adults can also be treated for the condition.
Sometimes a child’s eyes do not work together as they should. One eye may be ‘lazy’, or wander in or out, or up or down (strabismus). In such a case, the brain receives a different image from each eye. The brain may switch back and forth between the two images, or it may turn off the weaker image.
Sometimes a child cannot see objects that are far away (near-sightedness) or objects that are close up (far-sightedness). A child can even be so far-sighted that both near and distant objects are blurred. If the front of the child’s eye (cornea) is irregularly curved (astigmatism), objects look blurry at all distances. However, these common childhood vision problems can almost always be corrected with glasses or contact lenses. In some cases, vision problems can lead to amblyopia if not corrected.
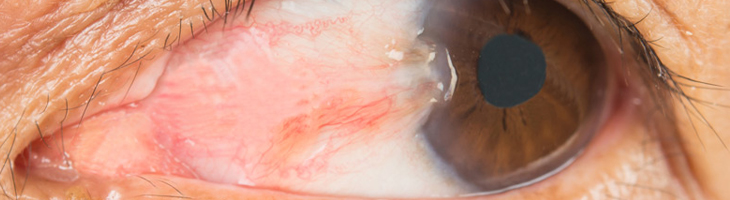
A pterygium is a growth of the conjunctiva or mucous membrane that covers the white part of your eye over the cornea. The cornea is the clear front covering of the eye. This benign or noncancerous growth is often shaped like a wedge. A pterygium usually doesn’t cause problems or require treatment, but it can be removed if it interferes with your vision.
The exact cause of pterygium isn’t known. One explanation is that too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can lead to these growths. It occurs more often in people who live in warm climates and spend a lot of time outdoors in sunny or windy environments. People whose eyes are exposed to certain elements on a regular basis have a higher risk of developing this condition. These elements include:
A pterygium doesn’t always cause symptoms. When it does, the symptoms are usually mild. Common symptoms include redness, blurred vision, and eye irritation. You might also feel a burning sensation or itchiness. If a pterygium grows large enough to cover your cornea, it can interfere with your vision. Thick or larger pterygium can also cause you to feel like you have a foreign object in your eye. You might not be able to continue wearing contact lenses when you have a pterygium due to discomfort.
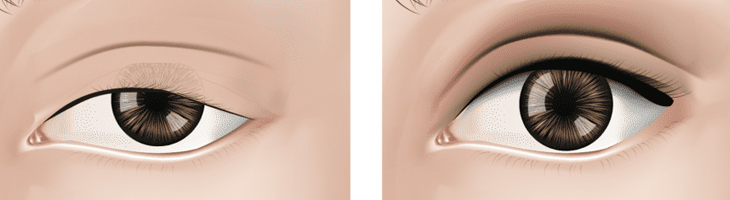
“Ptosis” means drooping. When the upper eyelid droops, it is called blepharoptosis, or upper eyelid ptosis.
There are several reasons an eyelid might droop. Some babies are born with ptosis in one or both eyelids. These children must have a thorough eyelid examination.
Ptosis can occur later in life if the muscles or ligaments that normally raise the eyelid are weakened by injury or disease. Sometimes the drooping is a result of damage to the nerves that control the eyelid muscles.
Most ptosis just happens with aging. As a person ages, the skin and muscles of the eyelids stretch and weaken. Sometimes, previous eye surgery speeds up this change because the instruments used to keep the eye open during surgery can stretch the eyelid.
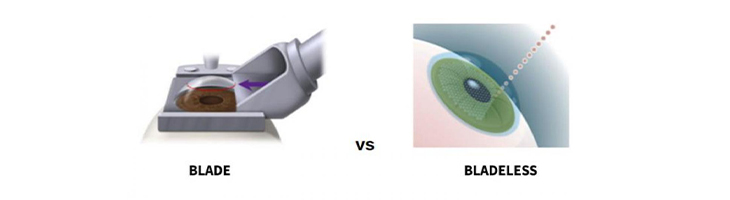
Intralase Lasik – Bladeless Or Blade Free Lasik
Intralase Lasik – Bladeless Or Blade Free Lasik
Intralase is a 100% Blade - free approach using ultra high precision Femtosecond Laser for creating the corneal flap with more safety and accuracy. By eliminating the hand held Microkeratome blade used in traditional LASIK for corneal flap creation, patients enjoy highest level of safety. With Intralase, using a computer controlled laser the surgeon delivers rapid pulses of light to a pre-programmed depth and position within the cornea. Also Intralase is able to treat patients with thin corneas which otherwise would have been turned down for Bladed LASIK.
The Intralase Method gives your doctor an extremely high degree of surgical control for exceptional outcome. Millions of procedures have been performed safely and efficiently using the Intra Lase Lasik technique with excellent results.
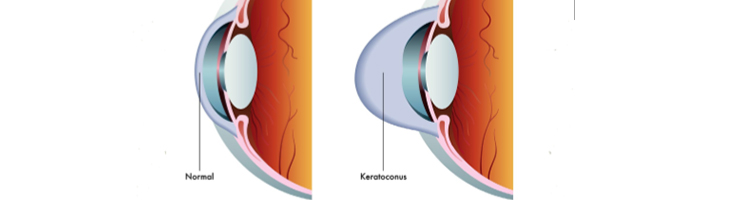
Cornea is the first coat of eye which is transparent circular structure. Functionally it acts as a lens responsible for focusing rays inside the eye. It is an important optical structure through which rays of light enter the eye. Any damage or injury to this delicate structure can lead to permanent loss of corneal transparency or in other words cause clouding and opacification. Loss of corneal transparency prevents the entry of light rays into the eye and reduces vision. In cases of severe of damage, this can cause total loss of vision making the person visually handicapped. There are other conditions also such as malnutrition, Vitamin A deficiency, infection, certain corneal diseases such as ‘keratoconus’ and ‘corneal degeneration’, which can cause corneal blindness. Corneal disease is third largest cause of blindness or low vision in Indian population. Corneal disorders encompass a wide spectrum of diseases most common of these are pterygium, Keratoconus, corneal dystrophy, corneal tears, corneal oedema , infective keratitis, contact lens related keratitis, allergic keratoconjunctivitis, each of these diseases need methodical approach and specialized care.
Pterygium is a veil like lesion that usually occurs in exposed part of white of the eye. This grows slowly over the cornea (the central black portion) and can obstruct vision or deteriorate vision by inducing cylindrical power.

Contoura vision is an advanced laser treatment for removal of spectacle numbers. Contoura vision also corrects irregularities in the cornea in addition to correcting glass numbers. This results in better quality of vision and sharp and crisp vision. It is a US FDA approved procedure. It corrects the power of glasses by treating at the visual axis thereby providing the sharpest possible vision. It is a painless stitchless procedure without the need of any injection, bandage or hospitalization. It improves the smoothness of the corneal surface . It uses a special equipment called the topolyser which marks the corneal irregularities thereby enhancing the sharpness of vision and making the cornea an optically perfect surface.
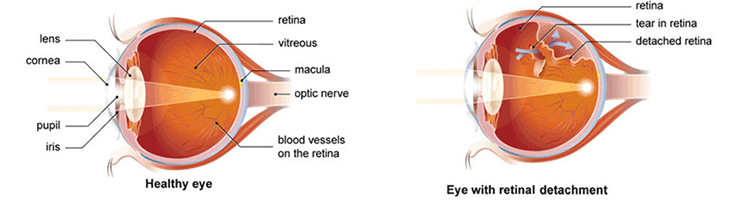
Retina is like the film in a camera. Retina is the third and inner coat of the eye which is a light-sensitive layer of tissue. When the focused light hits the retina, a picture is created and sent to the brain through the optic nerve (the nerve of the eye), thus giving us vision. Sometimes part of the retina either tears, pulls away or detaches from the back of the eye; when this occurs that part of the retina cannot gather light ans results in vision loss.
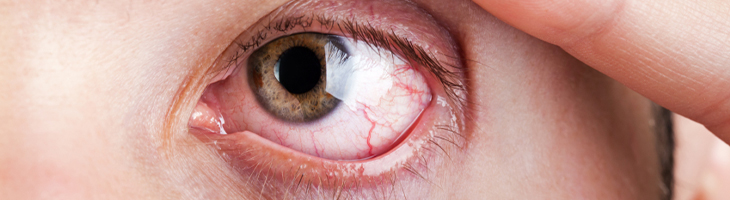
Dry eye syndrome is caused by a chronic lack of sufficient lubrication and moisture on the surface of the eye. Consequences of dry eyes range from subtle but constant eye irritation to significant inflammation and even scarring of the front surface of the eye. Dry eyes are very common, and dry eye syndrome is a major reason for visits to the eye doctor.
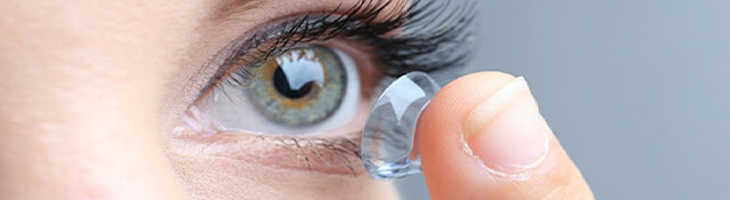
Advancements in contact lens technology offer the potential for successful contact lens wear to most of our patients. Contact lenses not only enhance visual acuity and appearance, but also improve performance in different visual tasks; helps avoid fogging of glasses in different environments, and also improve performance of other fast activities like sports.
Dispensing of different types of regular contact lenses – daily wear and extended wear Soft Disposable Lenses, Soft Conventional Lenses, Rigid Gas Permeable Lenses, Cosmetic lenses, Prosthetic lenses, and Bandage contact lenses
Dispensing Specialty Contact Lenses – Scleral Contact Lenses, Soft Toric Lenses, Rose-K Lenses for Keratoconus, Bifocal Contact Lenses, Piggyback Lenses for Keratoconus, Soft-perm lenses
Dispensing of appropriate Contact Lens Solutions for different type of lenses